Samplers principle of operation
Precise quality check of coal, biomass and other loose materials
Certified for compliance with standards ISO13909.
Samplers manufactured by Testchem are used for automatical sampling of
- loose samples materials in power plants and thermal power plants,
- to collect aggregate in cement plants, sand mines
- waste materials in ironworks and others.
Full automation of the process provides a representative sampling from moving conveyor belts (PSM, PSM-Z) or trucks and railcars (PSM-W).
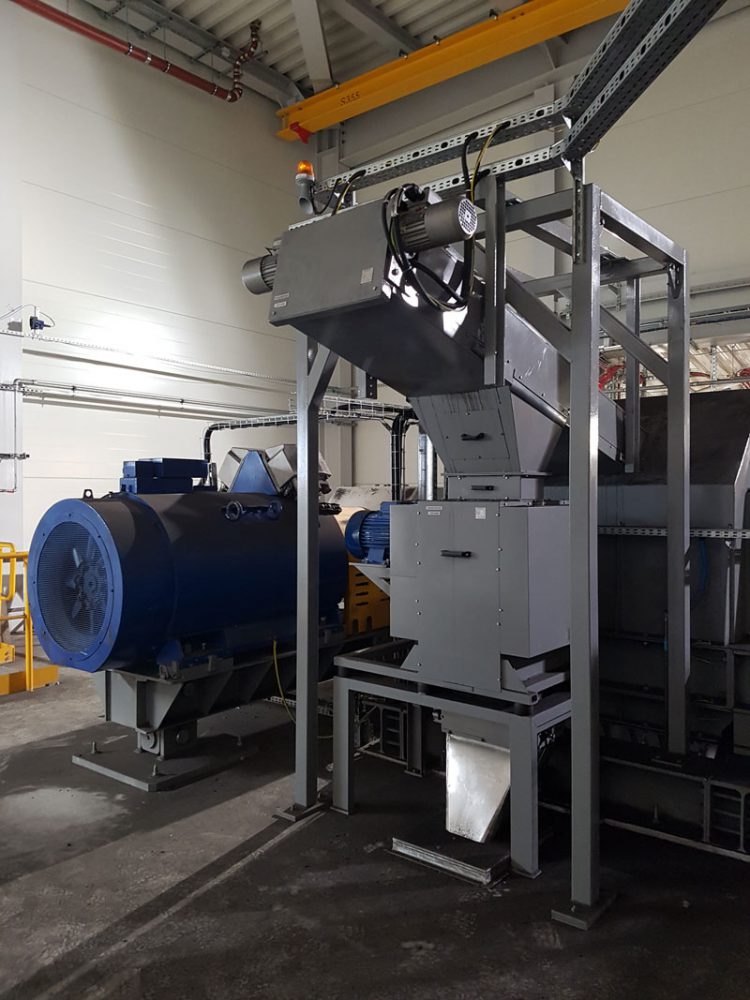
Principle of operation PSM – drawer sampler
- Drawers cross the coal stream in the transfer place between the conveyor belts, draw a sample in amount of about 3kg and throw it into the roll crusher.
- Next comes the crushing (4-roller crusher reduces grain 16x).
- There is a sample splitter of various degrees of separation under the crusher.
- Laboratory sample with a grain size <3mm is collected in a receiving reservoir.
- Excess sample is transported back to the conveyor belt below.

Principle of operation PSM-Z – scraping sampler
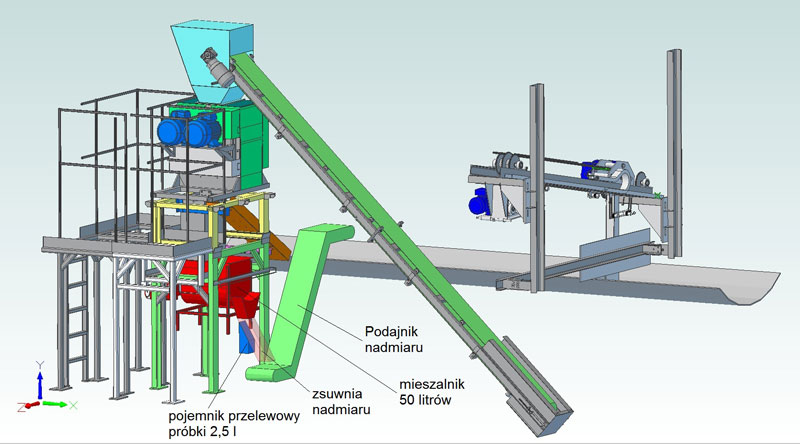
- Movable arm ending with a scoop cuts the coal stream across the working conveyor belts, gathers a sample in amount of about 3 kg and throws it on the conveyor belt transporting the sample to the roller crusher.
- Next comes the crushing (4-roller crusher reduces grain 16-fold).
- There is a sample splitter of various degrees of separation under the crusher.
- Laboratory sample with a grain size <3mm is collected in a receiving reservoir.
- Excess sample is transported back to the conveyor belt below or any other place.
Principle of operation PSM-W – drilling sampler
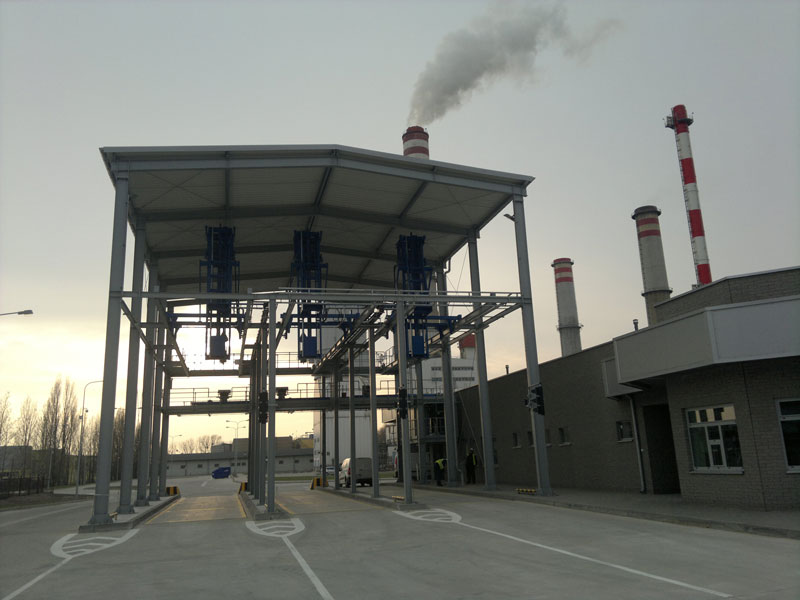

- Entering the power plant a driver chooses the nearest free position for sampling.
- After entering the vehicle scale the car is positioned by a system of sensors and lights.
- After leaving the cab driver confirms readiness for weighing and sampling by scanning magnetinc card.
- Chassis moves the drilling rig to a randomly selected location along the cargo space of the car.
- On reaching the drilling spot the process of sampling is being paused (so called pit stop). An image of drilling rig is transmitted with system of cameras into the sample preparation’s room to the desktop of the verifier, which confirms the correctness of the position.
- Afterwards the drill is activated and penetrates the random depth in cargo area of the vehicle.
- At the end of the sampling cycle chassis moves the drill to the unloading place. The extracted material reaches the mill with divider. Grinded sample is next transported by a scrap remover to the separate bag for packing and heat sealing, located in the sample preparation’s building.
- Staff seales the bag with biomass and puts a sticker with the description of supplier and type of material on it. This makes the green exit light turn on.
- To end up the process the driver has to get confirmation of being weighed on the exit scales.